LLM in Everyday Life: From the Keyboard of Your Phone to ChatGPT
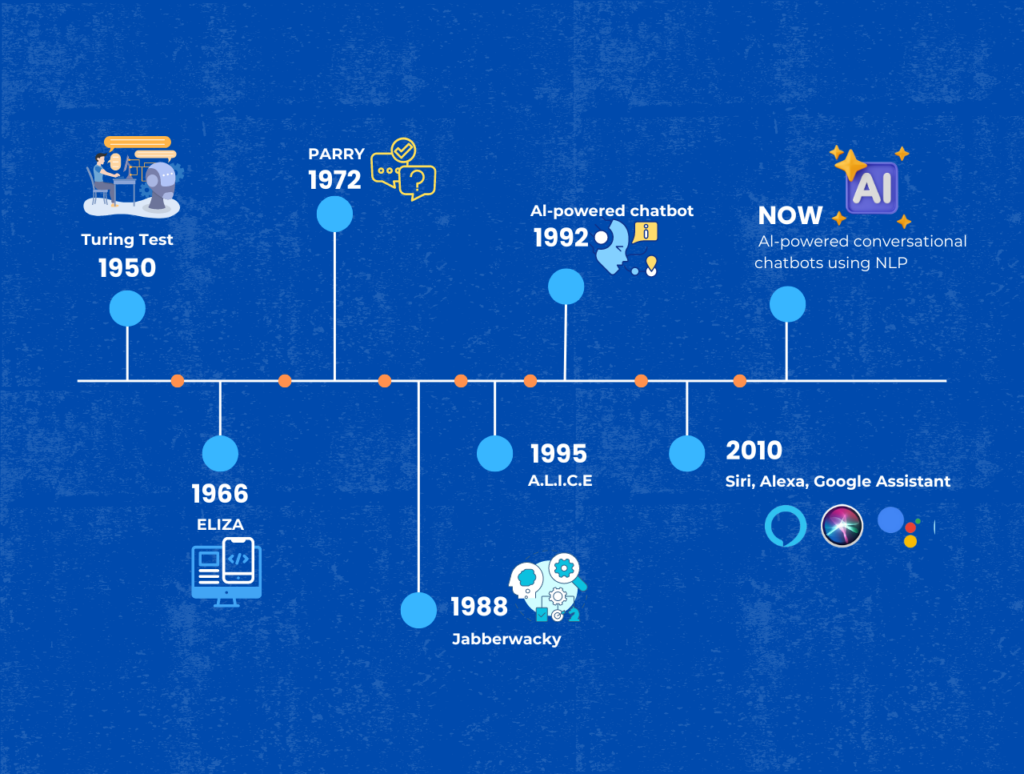
In today’s fast-paced world, technology is seamlessly woven into the fabric of our daily lives. One of the most significant advancements in recent years is the development of Large Language Models (LLMs). These powerful AI systems are transforming the way we interact with technology, often without us even realizing it. From the predictive text on your phone to sophisticated chatbots like ChatGPT, LLMs are becoming indispensable tools in our digital landscape. Let’s explore how LLMs work and where you can witness their magic in everyday life. What are Large Language Models? Large Language Models, or LLMs, are advanced AI systems designed to understand, interpret, and generate human language. They are trained on vast amounts of text data, allowing them to predict and generate text that is contextually relevant and coherent. LLMs like OpenAI’s GPT-3 have billions of parameters, making them capable of understanding complex language nuances and producing human-like text. The Magic Behind Your Smartphone Keyboard One of the most common places you encounter LLMs is right at your fingertips – the keyboard on your smartphone. Ever noticed how your phone suggests the next word while you’re typing a message? That’s an LLM at work. These predictive text features use sophisticated algorithms to analyze your typing habits and predict the next word or phrase, making your typing experience faster and more intuitive. Virtual Assistants: Your AI Companions Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are another prime example of LLMs in action. These AI-powered assistants rely on LLMs to understand your voice commands, process the information, and provide accurate responses. Whether you’re asking for the weather forecast, setting a reminder, or playing your favorite song, LLMs are the brains behind the operation, making these interactions feel natural and effortless. ChatGPT: Conversations with AI Chatbots like ChatGPT represent one of the most advanced applications of LLMs. These chatbots can engage in meaningful and coherent conversations, providing information, answering questions, and even offering companionship. ChatGPT, for example, can understand context, maintain the flow of conversation, and provide responses that are remarkably human-like. This makes it an invaluable tool for customer service, education, and entertainment. Enhancing Customer Experiences Businesses are leveraging LLMs to enhance customer experiences in various ways. E-commerce platforms use chatbots to assist customers with their queries, provide product recommendations, and streamline the shopping experience. LLMs analyze customer data to offer personalized suggestions, making online shopping more efficient and enjoyable. Language Translation: Bridging Communication Gaps Language translation services have seen remarkable improvements thanks to LLMs. Tools like Google Translate utilize LLMs to provide real-time translation, allowing people from different linguistic backgrounds to communicate effortlessly. These models understand context and nuances, offering translations that are more accurate and natural. This capability is invaluable for travelers, global businesses, and anyone needing to bridge language barriers. Personalizing Your Content Feed Social media platforms and content recommendation systems use LLMs to personalize your feed. By analyzing your interactions, preferences, and behavior, LLMs curate content that aligns with your interests. Whether it’s the articles suggested on your news app, the videos on your YouTube homepage, or the posts on your social media timeline, LLMs ensure that you receive content that resonates with you, enhancing your online experience. Automating Routine Tasks LLMs are also adept at automating routine tasks. Email platforms, for instance, use AI to suggest responses, sort emails, and even draft messages. This automation saves time and increases productivity by handling repetitive tasks, allowing you to focus on more important activities. Enhancing Creativity and Writing For writers, LLMs can be a source of inspiration and assistance. Tools like Grammarly and other AI-driven writing aids use LLMs to check grammar, suggest style improvements, and even generate content ideas. These tools help writers produce polished and compelling content, whether for professional or personal use. In Education: Personalized Learning Assistants Educational platforms are harnessing the power of LLMs to create personalized learning experiences. AI tutors can provide tailored assistance, answer student queries, and offer resources based on individual learning styles and needs. This personalization makes learning more effective and engaging, helping students achieve better outcomes. Healthcare: Better Patient Interaction In healthcare, LLMs are being used to improve patient interactions and streamline administrative tasks. AI-powered chatbots can answer patient queries, schedule appointments, and provide information on medications and treatments. This use of LLMs enhances patient care and reduces the burden on healthcare professionals. The Future of LLMs: Continuous Improvement The applications of LLMs are vast and continually evolving. As these models become more sophisticated, their integration into our daily lives will only deepen. Future advancements might include even more intuitive virtual assistants, smarter recommendation systems, and further innovations that we can’t yet imagine. Embracing the AI-Driven World Large Language Models are quietly revolutionizing our everyday lives, making interactions with technology more seamless and intelligent. From the keyboard on your phone to sophisticated chatbots like ChatGPT, LLMs are enhancing our digital experiences in numerous ways. As we continue to embrace and integrate these technologies, the potential for improving productivity, personalization, and convenience is boundless. Stay tuned to see how LLMs will continue to shape our world. At Nuclay Solutions, we specialize in leveraging advanced AI technologies, including Large Language Models, to transform businesses and enhance user experiences. Whether you’re looking to integrate AI chatbots, automate tasks, or personalize customer interactions, our expert team is here to help. Contact us today to learn how we can bring the power of LLMs to your business and drive innovation in your everyday operations.